Earth's lowly rumble
Earth is an incredibly noisy stead. Avalanches roar down mountains, volcanoes rumble, and hurricanes blast through coastal areas. And while at that place's a whole range of sounds that hoi polloi hind end hear, there are also Earth sounds that are too David Low for the human spike to weft up.
 |
| TV crews postponemen for Mount St. Helens to break open. Sound at low frequencies that people arse't pick up could provide a warning that much a unstable eruption is almost to take plac. |
| Kate Ramsayer |
These silent sounds, operating room infrasound, are vocation to some scientists. These researchers are using special microphones to eavesdrop along infrasound created by the creation around us. The noisemakers include volcanoes, tsunamis, hurricanes, and even the turbulence that shakes airplanes.
"We'rhenium learning more about how the planet operates by listening," says Michael A. Hedlin. He studies sounds at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography in Atomic number 57 Jolla, Kaliph.
Low-down notes
Comparable complete types of sound, infrasound travels in waves. The sound waves have different heights, or amplitudes, which make them louder operating room softer. They also have different wavelengths, measured from the crest of peerless wave to the upper of the next. And they have different frequencies, measured by the enumerate of crests that pass away a particular position per second.
Short, rapid waves make high-pitched sounds, like a teapot's whistle. Long, slow waves make low-pitched-inclined sounds, like a bass guitar in a rock lo. And below the lowest note on a bass, below what people can hear, there's infrasound.
 |
| An elephant generates and probably detects infrasound. |
Infrasound is created when something, much as a bomb explosion operating theatre an earthquake, sets a large amount of ventilate in motion. The resulting sound waves travel through the air, sometimes for thousands of kilometers.
Scientists originally started studying infrasound to make sure as shootin faraway countries weren't examination nuclear bombs. Now, they're using infrasound to check for raw events.
"We'rhenium finding totally these exotic sources [of infrasound] that we hadn't thought of earlier," Hedlin says.
Tsunami sounds
One of those infrasound sources is a gigantic wave called a tsunami. "We didn't live that a tsunami produces infrasound," says John Milton Garcés. He runs the infrasound laboratory at the University of Hawaii, Manoa.
 |
| Earthquakes subordinate the ocean can generate tsunamis. Particular instruments happening buoys, much as this one, can detect the resulting waves. |
| National Pelagic and Part Administration |
When a heavy earthquake occurred turned the coast of Indonesia in December 2004, for instance, it sent a deadly wave crossways the American Indian Sea. When Garcés looked at infrasound data that were registered all but the tsunami, He plant a big signal that corresponded to the wave. "It produced a wallop," he says.
In the last year, Garcés and his colleagues deliver picked skyward sounds from two many tsunamis. One was a Japanese tsunami that produced "beautiful infrasound," he says.
The researchers recently set up a tsunami infrasound project in Hawaii. "Whenever there's a tsunami, we'rhenium expiration to be look at it very carefully," Garcés says. The scientists hope to check how the giant waves produce infrasound, which is currently a whodunit.
Volcano rumbles
Garcés and others are also using infrasound to listen in happening volcanoes.
On the Sakurajima volcano in Japan, Garcés discovered that stronger and stronger infrasound signals led up to the vent's eruption in 1998. If this happens all the time, scientists could use infrasound patterns to warn people if a nearby volcano is about to blow, He says.
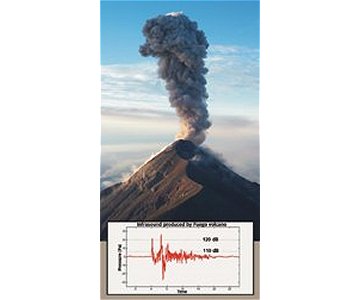 |
| The eruption of the Fuego volcano in Guatemala in 2003 generated rugged infrasound, mostly below a frequency of 10 hertz (cycles per second). The pressure readings express that the strong suit of these sound waves fundament reach the equivalent weight of 120 decibels (approximately the garishness of an ambulance siren, heavy machinery, or a rock concert). |
| Jeffrey B. Johnson, University of Hawaii at Manoa |
Detective work volcanic eruptions with infrasound would also be a useful tool for aeroplane pilots, because ash from an erupting volcano can perilously damage a plane's engines.
Infrasound stations are also keeping an ear on Backing St. Helens in Washington State. Hedlin can tell that gas is spumous prepared in the vent just aside looking the infrasound recordings.
The recordings besides detect miniature earthquakes inside the volcano that agitate air around, besides as other events whose causes are yet unknown. Infrasound gives researchers a more dispatch picture of how volcanoes solve, Hedlin says.
And scientists are always listening for parvenu things to inquire, Hedlin adds.
Hedlin has transcribed infrasound coming from sprites, which are short flashes of phosphorescent in the atmosphere in a higher place thunderclouds. He's likewise planning to set up a station to study winds off the coast of Africa, where hurricanes begin to form. To listen to the speeded-risen sound of a fairy (so that you can hear it), click hither.
 |
| The northern lights (auroras) generate infrasound aside pushing the surrounding air outward. |
| Collection of Dr. Herbert Kroehl, NGDC, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration |
Other researchers are using infrasound to detect avalanches, the aurora borealis, ocean waves, rough air out that causes airplane turbulence, and mountains shaking from earthquakes.
Animal calls
While people are deaf to infrasound, other animals appear to habituate it to communicate. When elephants trumpet, for example, they likewise produce infrasound that potty hand down other elephants as far as 10 kilometers away, researchers discovered.
Elephants might smooth pick up up these low rumblings through their feet, says Caitlin E. O'Connell-Rodwell. She's a man of science at Stanford University in California.
Other researchers take recommended that whales, rhinos, and big birds named cassowaries arse create or pick up infrasound. Even few dinosaurs might have had this ability.
 |
| A cassowary power lift up ultrasonic signals with its casque, a mysterious structure along top of its head. No one is yet foreordained what this structure is for. |
| Andrew L. Mack, Wildlife Conservation Society |
To boot, it's feasible that people can discover infrasound in special shipway. When elephants trumpet, "it's such a all-powerful, low-frequency fathom," O'Connell-Rodwell says. "You really feel it resounding in your chest."
In one experimentation, researchers in England played infrasound during a music performance. Although listeners couldn't hear the super-crushed notes, they seemed to take stronger emotions during the performance than did people who detected medicine without infrasound.
On that point for sure seems to be more to infrasound than meets the spike.
Going Deeper:
Extra Information
Questions some the Clause
Word Find: Infrasound
0 Response to "Earth's lowly rumble"
Post a Comment